In recent years, the cutting tool market has witnessed steady growth driven by the expansion of construction, furniture manufacturing, renovation work, and light industrial processing. Among the many products discussed in trade journals and industry events, the TCT Circular Saw Blade from fangda-tools has attracted attention for its role in shaping how workshops and factories approach efficiency. While the industry constantly evolves, certain equipment types maintain their relevance because they address practical challenges at a predictable and stable level. This type of blade is one example, and its industrial influence can be seen across diverse working environments.

Discussions around tool selection often revolve around durability, operational consistency, and adaptability. With more enterprises focusing on cost control and workflow optimization, understanding what differentiates various cutting blade categories has become essential. The improved awareness within the global tool market has also encouraged suppliers and manufacturers to publish clearer explanations of tool structures and their intended applications. As a result, more professionals and hobbyists alike have begun evaluating what these blades offer and how brands such as fangda-tools position them within the broader landscape.
1. What Defines a TCT Circular Saw Blade in Industrial Use
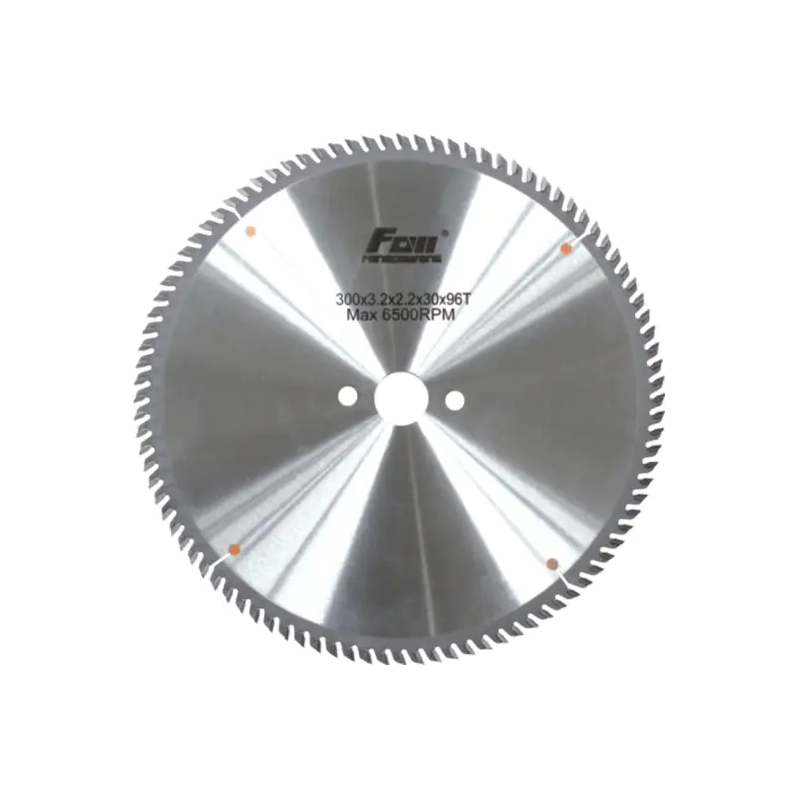
A TCT, or tungsten carbide tipped blade, is widely recognized in the equipment sector for its multi-material compatibility and steady cutting behavior. Unlike traditional blades made from single metal compositions, TCT blades integrate carbide tips along the edge to support service performance over extended periods. This structure aims to help maintain a consistent rotational cut even during demanding usage cycles.
Industrial publications often describe this tool as a hybrid design that balances strength and adaptability. It appears in job sites and woodworking shops, as well as metalworking areas for specific controlled tasks. This versatility has led procurement teams to consider it an informed choice for mixed-material processing, especially when operators require smoother workflow transitions.
The TCT Circular Saw Blade is frequently included in purchasing lists when factories plan upgrades because it helps support productivity without requiring major changes to existing equipment. As new machinery standards emerge around safety, vibration control, and environmental responsibility, this blade type continues to align with regulatory expectations by supporting stable operating patterns.
2. Why Many Professionals Evaluate This Blade Structure Carefully
Professionals in carpentry, installation work, and fabrication often face bottlenecks that stem from uneven cuts, tool wear, or surface tearing. These performance inconsistencies can slow down production timelines and affect project alignment. The carbide-tipped configuration is one response to those practical concerns, as it aims to help maintain edge quality through repeated cycles of use.
Attention to tool geometry also plays a central role. Manufacturers frequently adjust the number of teeth, angle settings, and plate thickness to address noise control, dust management, and material compatibility. In industry exhibitions, experts regularly note that these fine adjustments influence the surface finish of each cut, which can reduce the need for secondary processing.
While no single tool category fits every scenario, many workshops choose the TCT structure because it reduces unexpected interruptions. This has encouraged market analysts to observe a rising trend in its adoption for both large production lines and mobile contractor setups.
3. How the Market Views Multi-Purpose Cutting Tools Today
The tool industry has shifted from single-use equipment toward hybrid solutions that address multiple job types. Rising labor costs and the drive toward integrated workflow systems have pushed businesses to analyze total tool value over time. In this environment, multi-purpose blades generate attention because they help simplify inventory complexity.
Two main factors shape purchasing decisions:
- Material Diversity :Companies often handle more than one type of material. Having a blade that assists in managing different surfaces with steady control supports project planning.
- Workforce Skill Level :Skilled technicians can adapt to various blade types, but workforce variability means that many companies prefer equipment that supports predictable results even for intermediate-level operators.
The introduction of more automated saw units in factories has also encouraged the selection of reliable blade structures. Industry analysts anticipate continued demand, particularly in sectors where both wood and certain metals must be processed without constant tool changes.
4. Industry Conversations Surrounding the TCT Circular Saw Blade
The fangda-tools product range has frequently appeared in trade discussions centered on workflow efficiency and material compatibility. Many distributors note that professionals evaluate this blade for its potential to handle both wood-based materials and certain controlled metal types within moderate cutting environments. The brand's ongoing presence in international exhibitions has contributed to its visibility among procurement teams.
When companies compare cutting solutions, they often examine how a blade supports consistent feed rates and predictable kerf behavior. The TCT Circular Saw Blade offered by fangda-tools fits into conversations around versatile operation because its structure aims to limit friction while maintaining a steady cutting path. Articles in manufacturing journals have pointed out that such characteristics help reduce manual correction during multi-step projects.
Furthermore, service life expectations influence decisions for workshop upgrades. Businesses prefer tools that maintain their profile shape over time, as this directly affects the precision of repetitive cuts. Publicly available technical diagrams of this blade type emphasize tooth geometry and optimized plate balance, both of which contribute to smoother workflow management.
5. Is This Blade Suitable for Both Wood and Controlled Metal Cutting
Across online forums and industrial newsletters, professionals discuss how modern carbide-tipped blades may serve dual-purpose environments. The TCT Circular Saw Blade design is often part of these conversations because it aims to maintain tip stability during transitions between soft and firm materials.
For wood applications, the blade assists in maintaining edge quality on plywood, solid panels, composite boards, and laminated structures. For controlled metal use cases, such blades are sometimes chosen for light-duty tasks involving thin pipes, aluminum profiles, or mild materials. It is important to evaluate the specific work conditions, as not all metals require the same blade geometry. Still, many workshops appreciate the flexibility this structure provides, which helps streamline project sequences by reducing tool changes.
In mixed-material production facilities where both wood and light metals appear in alternating tasks, procurement managers often select a blade category that supports operational continuity. This is one reason why discussions around the product line have remained active in recent years.
6. Common Cutting Challenges and How This Blade Helps Address Them
Many manufacturing processes face recurring issues that slow down workflow. The following list summarizes some typical problems and the ways in which a carbide-tipped blade configuration helps address them in a practical and industry-compliant manner.
Frequent Cutting Issues
Below is an overview of general challenges seen across workshops:
| Cutting Challenge |
Industry Observation |
How a TCT Blade Assists |
| Edge tear-out on wood |
Occurs during high-speed cuts |
Carbide tips sustain edge alignment |
| Heat buildup |
Leads to surface discoloration |
Optimized geometry helps manage heat distribution |
| Tool wear during metal cutting |
Causes rough surfaces |
Harder tips resist deformation |
| Inconsistent kerf lines |
Affects assembly accuracy |
Balanced plate construction supports stable movement |
| Need for frequent blade changes |
Reduces efficiency |
Multi-material compatibility reduces interruptions |
This table provides only a simplified snapshot of broader industry patterns, but it reflects why these blades continue to generate interest among technicians and procurement specialists.
7. The Role of Carbide Technology in Current Industry Trends
Carbide-tipped solutions are part of larger tool manufacturing trends that emphasize sustainability, operational continuity, and reduced waste. As more factories aim to align with modern environmental and occupational guidelines, choosing equipment that supports predictable performance becomes essential.
Today's market trends highlight three important factors:
- Material Conservation :Cleaner cuts help reduce waste during trimming and fitting operations.
- Safety Compliance :Stable cutting reduces sudden blade binding scenarios that may affect operators.
- Equipment Longevity :Tools that maintain their structure over multiple cycles contribute to more efficient long-term planning.
Given these developments, carbide technology is expected to remain relevant as industries advance toward automation and smart workshop layouts.
8. Why Many Workshops Consider This Blade a Practical Option
A growing number of manufacturers evaluate cost efficiency not only through the initial purchase price but also through the stability and predictability of long-term performance. The TCT blade category aligns with these priorities because it supports consistent application across various tasks.
Shops that handle panel furniture, outdoor construction, interior renovation, or small metal components often reference the same set of expectations:
- Predictable cutting patterns
- Manageable noise levels
- Controlled chip generation
- Adaptation to different saw units
- Reduction in downtime due to blade changes
These expectations shape procurement strategies, and many companies include the fangda-tools line in their market research because the brand invests in clear communication and steady product availability across international channels.
9. Final Thoughts on the Position of This Blade in the Global Cutting Tool Landscape
As the cutting tool industry continues to expand and diversify, the TCT structure remains prominently discussed in expert forums, trade events, and manufacturing reports. Its continued relevance stems from its multifaceted approach to project demands and its adaptability to different work environments.
Whether applied in woodworking, controlled metal processing, or hybrid fabrication scenarios, this blade type offers a balanced approach to workflow reliability. The TCT Circular Saw Blade by fangda-tools appears frequently in industry analysis not because of exaggerated claims, but because it aligns with modern working conditions and provides a stable foundation for structured production planning.
For readers following market developments or considering upgrades in their own workshop, keeping an eye on how this blade category evolves will help inform future decisions.