Woodworking Router Bits are indispensable tools in woodworking, widely used for slotting, trimming, carving, and joinery. Different types of router bits are suitable for different processing needs, and choosing and using them correctly not only improves work efficiency but also extends tool life. This article introduces the types, differences, speed settings, selection techniques, and common issues of router bits, helping woodworking enthusiasts better master this essential tool.

1. Main Applications of Woodworking Router Bits
Woodworking are primarily used for cutting, carving, and shaping wood. Common applications include:
Slotting: For making mortises, T-slots, and other structures.
Trimming: For chamfering, rounding over, or decorative edge treatment.
Carving: For creating complex patterns or relief effects.
Joinery: For finger joints, mortise-and-tenon, and other connection processes.
Router bits can be paired with different types of routers (handheld or table-mounted) and are widely applied in furniture manufacturing, flooring installation, and wooden crafts.
2. Common Types of Woodworking Router Bits
There are many types of bits, classified by function and structure as follows:
| Type |
Application |
Features |
| Straight Bit |
tSlotting, trimming, bottom cleaning |
Strong cutting force, suitable for straight cuts |
| Spiral Bit |
lotting, carving, fine trimming |
Smooth chip removal, reduces risk of burning wood |
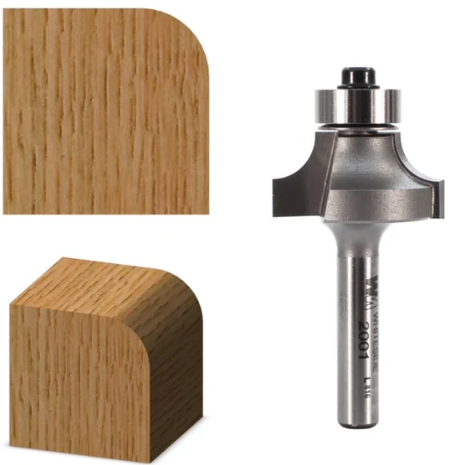
| Round-Over Bit |
Rounding edges |
Creates arcs of different radii
|
| V-Groove Bit |
Carving, V-shaped grooves |
Suitable for decorative lines and lettering |
| Mortising Bit |
Making mortises |
Specially designed for joinery processes |
| Edge-Forming Bit |
Decorative edge profiles |
Can produce complex patterns |
Among these, straight bits and spiral bits are the most commonly used. Their differences are:
Straight Bit: Straight cutting edge, suitable for fast cuts, but weaker in chip removal, which may cause overheating.
Spiral Bit: Helical cutting edge, smoother cutting, better chip evacuation, especially suitable for hardwoods and deep grooves.
3. How to Set the Speed of Router Bits?
The rotation speed of router bits directly affects the processing results and tool life. It usually needs to be adjusted according to the bit diameter and wood hardness:
| Router Bit Diameter (mm) |
Softwood (RPM) |
Hardwood (RPM) |
| 6–12 |
18,000–24,000 |
16,000–20,000 |
| 13–25 |
12,000–16,000 |
10,000–14,000 |
| 26–50 |
8,000–12,000 |
6,000–10,000 |
Notes:
The larger the diameter of the router bit, the lower the rotation speed should be, to avoid overheating and vibration.
When processing hardwood, reducing the speed appropriately can minimize tool wear.
4. How to Choose the Right Router Bit for Your Project
When selecting router bits, the following factors should be considered:
1.Processing Needs: Different tasks such as slotting, trimming, or carving require matching bit types.
2.Wood Type: Spiral bits are recommended for hardwood, while straight bits work well for softwood.
3.Cutting Depth: For deep grooves, choose a long-flute spiral bit.
4.Surface Quality Requirements: For fine carving, high-precision spiral bits or V-groove bits are recommended.
Example Selection Guide:
Making cabinet doors → Edge-forming bit
Cutting mortises → Mortising bit
Edge trimming → Round-over bit or straight bit
5. Lifespan and Maintenance of Router Bits
1. Service Life
The lifespan of router bits is affected by the following factors:
Frequency of use: High-frequency use accelerates wear.
Wood hardness: Hardwood causes more wear on the bit.
Speed setting: Excessive speed can lead to overheating and deformation.
Signs for Replacement:
Cutting efficiency drops significantly
More burrs appear on wood edges
Cutting edge shows noticeable wear or chipping
2. Cleaning and Maintenance
After each use: Clean wood chips with a soft brush to prevent resin buildup.
For long-term storage: Apply anti-rust oil and keep in a dry environment.
6. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
1.Incorrect speed (too high or too low) → Adjust according to the recommended speed chart.
2.Improper feed rate → Maintain steady, even feeding and avoid pauses.
3.Loose installation of the bit → Ensure the collet is firmly tightened to prevent vibration.
4.Neglecting chip removal → Clean wood chips regularly to avoid clogging.
Tips to Prevent Wood Burning:
Use spiral bits to improve chip evacuation.
Control feed rate to avoid prolonged friction.
Lower the speed appropriately to reduce heat buildup.
7. Why Choose Woodworking Router Bits?
Woodworking router bits, with their versatility, high precision, and efficient cutting ability, have become core tools in modern woodworking. Whether for professional carpenters or DIY enthusiasts, choosing and using router bits correctly can significantly improve both the quality of work and overall efficiency.
Through this guide, readers should now have a deeper understanding of the types, usage techniques, and maintenance methods for bits. In practice, selecting the right bit based on specific needs and following proper operating methods will ensure the best performance of the tool.